Allergies got you sneezing, itching, and feeling miserable? You’re not alone—millions worldwide struggle with allergies that disrupt daily life. From pollen and dust to food and pet dander, these invisible irritants can turn simple moments into battles. But understanding allergies is the first step toward relief. Let’s uncover what triggers them, how they affect your body, and what you can do to finally take control.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Allergies
Have you ever walked into a room, sneezed uncontrollably, and wondered why your body seems to rebel against harmless things like dust or pollen? That’s your immune system overreacting to what it mistakenly thinks is a threat—an allergy in action. Allergies have become one of the most common chronic conditions in the world, affecting millions of people across all ages and backgrounds.
Allergies are more than just a seasonal nuisance; they’re a complex immune response that can range from mildly irritating to potentially life-threatening. In today’s world, with pollution, processed foods, and changing environmental conditions, the number of people suffering from allergies is skyrocketing. Understanding allergies is no longer optional—it’s essential for managing your health.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what allergies are, how they happen, what triggers them, and most importantly, how you can manage and even prevent them. By the end, you’ll have a deep understanding of why your body reacts the way it does and what you can do about it.

What Exactly is an Allergy?
An allergy is your immune system’s overreaction to a substance that is typically harmless. These substances, known as allergens, can be found anywhere—from the food you eat to the air you breathe. When your body encounters an allergen, it mistakenly identifies it as a harmful invader, much like a virus or bacteria. This sets off a chain reaction involving antibodies called Immunoglobulin E (IgE).
When IgE antibodies bind to allergens, they trigger the release of chemicals such as histamine from certain immune cells. Histamine is the culprit behind most allergy symptoms—it causes itching, sneezing, swelling, and other classic signs of an allergic response.
Interestingly, allergies are not the same for everyone. Some people might get a mild rash from peanuts, while others could go into anaphylactic shock—a life-threatening reaction that requires immediate medical attention.
Allergies can also develop at any age. A person might go through childhood allergy-free and suddenly find themselves allergic to seafood or pollen in adulthood. Genetics, environment, diet, and lifestyle all play a role in how and when allergies develop.
How the Immune System Reacts to Allergens
Your immune system’s job is to protect you from dangerous pathogens. However, in people with allergies, this defense mechanism goes into overdrive. When you’re exposed to an allergen, your body misinterprets it as harmful. The first time you encounter it, your immune system produces IgE antibodies specific to that allergen. These antibodies attach to immune cells called mast cells and basophils.
The next time you’re exposed to the same allergen, it binds to those IgE antibodies, causing the mast cells to release histamine and other inflammatory chemicals. This release leads to the well-known allergy symptoms—runny nose, watery eyes, itchy skin, and sometimes even difficulty breathing.
Think of your immune system as an overly protective guard dog—it means well, but sometimes it attacks when there’s no real danger. And once your immune system “learns” to react to an allergen, it’s ready to overreact again the next time it encounters it.
Certain factors like stress, poor diet, lack of sleep, and exposure to pollutants can further amplify your immune response, making allergic reactions worse or more frequent.
Common Types of Allergies
Allergies come in many forms, and understanding their types can help you manage symptoms more effectively. While some allergies cause only mild irritation, others can trigger serious health complications. Let’s explore the most common types.
Food Allergies
Food allergies are among the most recognized types, often developing in childhood but sometimes appearing later in life. The most common culprits include peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, eggs, milk, soy, and wheat. When someone with a food allergy consumes even a small amount of the allergen, their immune system reacts almost instantly. Symptoms can range from mild itching and swelling of the lips to severe anaphylaxis, which requires immediate medical care.
Food allergies are often confused with food intolerances, but they’re not the same. A food intolerance involves the digestive system, while an allergy involves the immune system. For instance, lactose intolerance causes digestive discomfort, not an immune reaction.

Seasonal (Pollen) Allergies
Also known as hay fever or allergic rhinitis, seasonal allergies flare up when certain plants release pollen into the air. Trees, grasses, and weeds are major pollen producers, especially during spring and fall. Symptoms typically include sneezing, nasal congestion, watery eyes, and fatigue.
For many people, seasonal allergies can make even a beautiful spring day miserable. The good news? Over-the-counter antihistamines and nasal sprays often provide relief, and staying indoors during high pollen counts can help minimize exposure.

Skin Allergies
Common causes include contact with irritants such as soaps, detergents, cosmetics, or certain metals like nickel. Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is another skin-related allergic condition, often linked to asthma or hay fever.
Treating skin allergies usually involves identifying and avoiding the triggering substance. Topical creams, antihistamines, and moisturizers can soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.

Drug Allergies
A drug allergy occurs when your body’s immune system reacts negatively to a medication. Penicillin and other antibiotics are common culprits, though any drug can potentially cause an allergic reaction. Symptoms can appear within minutes or hours of taking the medication and may include hives, rash, or swelling.
In severe cases, a drug allergy can lead to anaphylaxis—a medical emergency that demands immediate attention. Always inform your doctor about any drug allergies before taking new medications.
Insect Sting Allergies
For most people, an insect sting causes temporary pain and mild swelling. However, for those allergic to insect venom (like bees, wasps, or hornets), the reaction can be life-threatening. Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and swelling of the face or throat.
People with severe insect allergies should always carry an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) and seek immediate medical care after a sting.
Most Common Allergens Around Us
You’d be surprised at how many allergens surround us daily. They hide in our homes, food, and even the air we breathe. Knowing where allergens come from is the first step in controlling exposure.
Some of the most common allergens include:
- Pollen: Released by trees, grasses, and weeds, pollen is one of the top culprits for seasonal allergies.
- Dust mites: These microscopic bugs thrive in bedding, carpets, and upholstery.
- Pet dander: Proteins in pet saliva, urine, and skin flakes can trigger allergic reactions.
- Mold: Fungi that grow in damp areas like bathrooms and basements release spores that can cause respiratory issues.
- Certain foods: Peanuts, shellfish, dairy, and eggs are the most common food allergens.
- Insect venom: Bee and wasp stings can cause allergic reactions.
- Latex: Found in gloves and medical equipment, latex allergies are common among healthcare workers.
Being aware of your environment and minimizing exposure—like using air purifiers, washing bedding regularly, and keeping pets out of bedrooms—can significantly reduce allergy symptoms.
Symptoms of Allergies
Allergic reactions can range from mildly uncomfortable to life-threatening. Recognizing the symptoms early can help prevent complications and ensure timely treatment.
Mild Allergy Symptoms
Mild allergic reactions might not seem like a big deal, but they can escalate if ignored. Common mild symptoms include:
- Sneezing and runny nose
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Skin rash or hives
- Nasal congestion
- Mild swelling (especially around the eyes or lips)
These symptoms can appear within minutes or hours after exposure to an allergen. Over-the-counter antihistamines and nasal sprays are often enough to provide relief.

Severe Allergy Symptoms (Anaphylaxis)
Anaphylaxis is the most dangerous form of allergic reaction. It can occur suddenly and progress rapidly, becoming life-threatening if not treated immediately. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Swelling of the throat or tongue
- Drop in blood pressure (causing dizziness or fainting)
- Rapid or weak pulse
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Loss of consciousness
If you or someone nearby experiences these symptoms, call emergency services right away. Epinephrine (adrenaline) should be administered immediately using an auto-injector, such as an EpiPen. Even after the injection, medical attention is essential because symptoms can recur.
How Allergies Are Diagnosed
Getting a proper diagnosis is key to managing allergies effectively. Self-diagnosis might lead to confusion or unnecessary dietary restrictions, so consulting an allergist is always the best route.
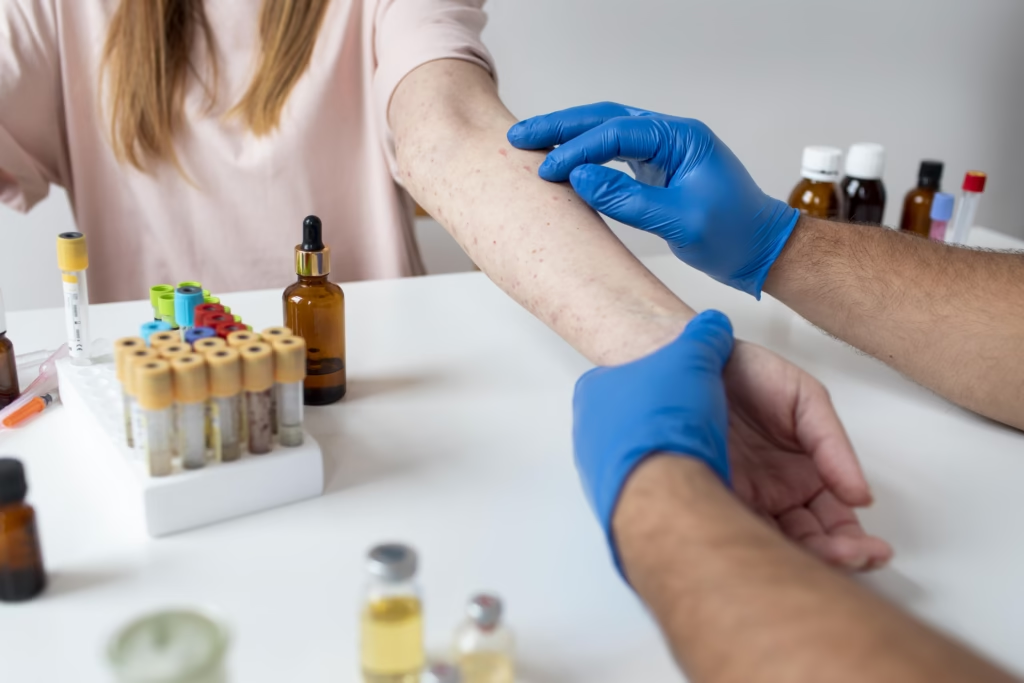
Skin Prick Tests
A skin prick test is one of the most common ways to identify allergens. Tiny drops of suspected allergens are placed on your skin, usually on the forearm or back. Then, the skin is lightly pricked to allow exposure. If you’re allergic, you’ll develop a small red bump or hive within 15 to 20 minutes.
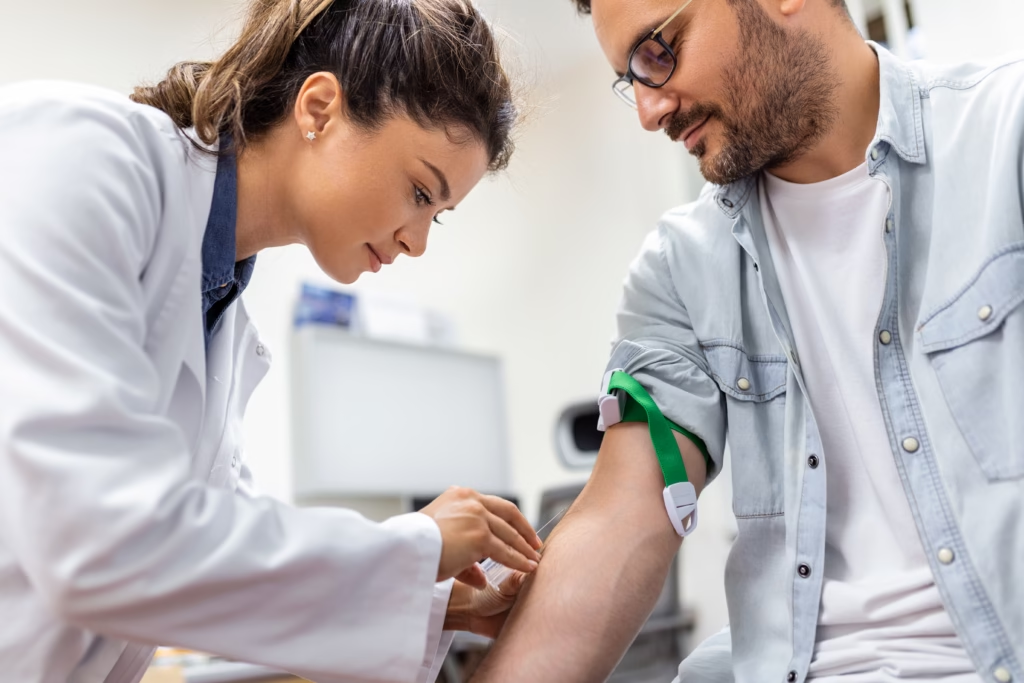
Blood Tests
A blood test, often called a specific IgE test, measures the amount of allergy-related antibodies in your blood. It’s useful for people who can’t undergo skin testing due to skin conditions or medication use.
Elimination Diet
For food allergies, an elimination diet can help identify the trigger. This involves removing potential allergens from your diet for a few weeks and then gradually reintroducing them while monitoring symptoms. It’s best done under medical supervision to avoid nutritional deficiencies.
Each diagnostic method has its advantages, and often, doctors combine them for the most accurate results.
Allergy Triggers You Might Not Know About
When we think of allergies, common culprits like pollen, dust, and peanuts often come to mind. But did you know there are several hidden triggers that can spark allergic reactions without you realizing it? These “stealth allergens” often go unnoticed and can make it difficult to pinpoint the real cause of your symptoms.
For instance, fragrances in perfumes, lotions, or cleaning products can cause sneezing, watery eyes, or even skin irritation. Many people are sensitive to artificial scents, especially those found in air fresheners and detergents. Similarly, household mold—which grows in damp areas like bathrooms, basements, or near leaky pipes—can release spores that trigger respiratory allergies and asthma-like symptoms.
Another surprising trigger is nickel, a metal used in jewelry, belt buckles, and even cell phones. Prolonged contact can lead to itchy rashes known as contact dermatitis. Certain chemicals in cosmetics such as parabens and preservatives also act as hidden allergens.
Even your workplace might be a source of unexpected allergens—printer toner, cleaning products, and industrial dust can cause allergic symptoms in sensitive individuals.
What’s more, weather changes and air pollution can worsen existing allergies. Cold air, humidity, or smog can irritate the nasal passages and heighten the body’s reaction to allergens already in the environment.
So, if your allergy symptoms persist even after removing common triggers, it might be worth investigating these lesser-known culprits. Keeping a symptom diary can help identify patterns and pinpoint what’s really causing your allergic flare-ups.
Difference Between Intolerance and Allergy
Many people confuse food intolerance with food allergy, but they’re quite different in how they affect the body. Understanding the distinction can save you from unnecessary worry—and help you get the right treatment.
A food allergy involves your immune system. When you eat something you’re allergic to, your body treats it like an invader and launches an immune response. This can cause hives, swelling, breathing problems, or even anaphylaxis in severe cases.
A food intolerance, on the other hand, involves the digestive system, not the immune system. It happens when your body struggles to digest certain substances. For example, lactose intolerance occurs when your body doesn’t produce enough of the enzyme lactase to break down lactose in dairy products. The result? Gas, bloating, and stomach cramps—but not an immune reaction.
The key difference is severity and system involvement:
| Condition | Involves Immune System? | Common Symptoms | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allergy | Yes | Hives, swelling, breathing difficulty | Can be life-threatening |
| Intolerance | No | Gas, bloating, diarrhea | Usually mild to moderate |
If you’re unsure which one you’re dealing with, allergy testing can provide clarity. While intolerances are uncomfortable, allergies can be dangerous—so knowing the difference could literally save your life.
Allergies in Children vs. Adults
Allergies can affect anyone, but they often show up differently in children than in adults. In kids, allergies tend to appear early—especially food allergies like milk, eggs, and peanuts. Some of these allergies fade with age, while others persist into adulthood.
Children’s immune systems are still developing, which might make them more reactive to certain allergens. Common symptoms in kids include eczema, chronic runny nose, sneezing, and digestive discomfort after eating specific foods. Parents often notice patterns—like a rash after eating strawberries or a coughing fit after playing with the family cat.
For adults, allergies might appear unexpectedly. You could live allergy-free for years and suddenly develop sensitivity to pollen or seafood. Lifestyle changes, stress, or long-term exposure to certain allergens can “trigger” new sensitivities later in life.
It’s also worth noting that asthma and allergies often go hand in hand, especially in children. Managing one usually helps control the other. Parents should work closely with pediatricians to identify and manage allergy triggers early, as untreated allergies can affect sleep, concentration, and even growth.
Both kids and adults can benefit from allergy testing and management plans tailored to their needs. The earlier allergies are detected, the easier it is to manage them effectively.
Effective Treatment Options for Allergies
When it comes to managing allergies, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. The right treatment depends on the type of allergy, its severity, and how often symptoms occur. Fortunately, modern medicine offers several effective options that can dramatically improve quality of life.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are the first line of defense for many allergies. They work by blocking the effects of histamine—the chemical responsible for itching, sneezing, and swelling. You can find antihistamines in tablets, liquids, or nasal sprays. Common brands include cetirizine, loratadine, and fexofenadine. These medications provide quick relief from mild to moderate allergy symptoms.
Corticosteroids
For more severe or persistent allergies, corticosteroids are often prescribed. These anti-inflammatory drugs reduce swelling and irritation in the nasal passages, skin, or airways. They come in the form of nasal sprays, creams, or oral medications.
Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
If medications don’t provide enough relief, allergy shots—also known as immunotherapy—may be the answer. This treatment gradually exposes your body to small amounts of the allergen, helping your immune system build tolerance over time. It’s a long-term commitment but can significantly reduce or even eliminate allergic reactions for some people.
Epinephrine for Severe Reactions
For people prone to anaphylaxis, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) is essential. Epinephrine quickly reverses severe allergic symptoms by relaxing the muscles in the airways and tightening blood vessels to maintain blood pressure.
The goal of treatment isn’t just to mask symptoms—it’s to help your body adapt and manage allergens more effectively. With the right combination of medication, lifestyle adjustments, and medical supervision, most people can live comfortably despite having allergies.
Natural Remedies for Allergies
While medications can provide fast relief, many people seek natural ways to manage allergies without relying solely on pharmaceuticals. Natural remedies can complement medical treatment and often focus on strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation.
1. Local Honey
A popular home remedy for seasonal allergies is consuming local honey. The theory is that small doses of pollen found in local honey can help your body build tolerance over time, similar to natural immunotherapy. While scientific evidence is limited, many allergy sufferers report that it eases their symptoms during pollen-heavy seasons.
2. Saline Nasal Rinse
A saline rinse or neti pot helps clear allergens, mucus, and irritants from your nasal passages. Using a saline solution can reduce nasal congestion, sneezing, and sinus pressure. Just be sure to use sterile or distilled water to avoid introducing bacteria into your sinuses.
3. Quercetin and Vitamin C
Quercetin is a natural plant compound found in apples, onions, and berries. It acts as an antihistamine by stabilizing mast cells, preventing them from releasing histamine. When combined with vitamin C, it can enhance immune function and help control allergic inflammation naturally.
4. Probiotics
Your gut health plays a major role in immune balance. Probiotics, found in yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods like sauerkraut, can improve your gut microbiome and potentially reduce allergic sensitivity. A balanced gut helps your immune system distinguish between harmful and harmless substances more effectively.
5. Herbal Remedies
Herbs such as butterbur, stinging nettle, and spirulina have shown promise in reducing allergy symptoms. Butterbur, in particular, may work similarly to antihistamines without causing drowsiness. Always consult a healthcare provider before using herbal supplements, especially if you take prescription medications.
6. Lifestyle Adjustments
Simple habits like showering after spending time outdoors, using HEPA filters in your home, and keeping windows closed during high pollen counts can make a noticeable difference.
While natural remedies aren’t a cure, they can enhance your overall well-being and help minimize allergic flare-ups. Consistency is key—over time, these small habits can create significant improvements in your body’s response to allergens.
How to Prevent Allergic Reactions
+ Avoiding exposure to allergens can save you from discomfort—and potentially dangerous reactions. Here are some practical prevention strategies that can make a big difference.
1. Keep Indoor Air Clean
Airborne allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and pollen often accumulate indoors. Use air purifiers with HEPA filters, vacuum regularly, and keep humidity levels below 50% to discourage mold growth. Wash curtains, bedding, and stuffed toys in hot water every week to remove allergens.
2. Control Pollen Exposure
If you have seasonal allergies, stay indoors when pollen counts are high, typically in the early morning or windy days. Keep windows and doors closed, and shower immediately after being outdoors to remove pollen from your skin and hair.
3. Watch What You Eat
For food allergies, always read labels carefully. Many packaged foods contain hidden ingredients like nuts, soy, or dairy. When eating out, inform the restaurant staff about your allergy to prevent cross-contamination. Carrying an emergency allergy card can also be helpful when traveling.
4. Manage Pet Allergies
If you’re allergic to animals, consider keeping pets out of bedrooms and using a HEPA vacuum to reduce dander. Bathing pets regularly can also decrease allergen buildup in their fur.
5. Avoid Harsh Chemicals
Switch to fragrance-free and hypoallergenic cleaning products and cosmetics. Chemicals in these items can trigger contact allergies or worsen respiratory symptoms.
6. Strengthen Your Immune System
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can support your immune system and reduce inflammation. Regular exercise and sufficient sleep also play a crucial role in maintaining immune balance.
Allergy prevention requires a proactive approach, but the payoff is worth it—less discomfort, fewer medications, and a better quality of life.
Living with Chronic Allergies
Living with chronic allergies can feel exhausting, especially when symptoms become part of your daily life. However, with proper management, it’s entirely possible to live comfortably and minimize disruptions.
Start by understanding your triggers. Keeping an allergy journal can help track what causes your symptoms and how severe they are. Once you know your triggers, it becomes easier to avoid or prepare for them.
Consistency in your treatment plan is crucial. If you’ve been prescribed medications like antihistamines or nasal sprays, take them regularly instead of waiting for symptoms to worsen. For people with severe allergies, always have an emergency action plan and carry necessary medications, including an epinephrine auto-injector.
It’s also important to maintain good indoor hygiene. Use allergen-proof bedding covers, vacuum frequently, and invest in a quality air purifier. Small changes like removing carpets or switching to hardwood flooring can also reduce allergen buildup dramatically.
Emotional well-being matters too. Constant sneezing, itching, or fear of reactions can affect mental health. Practices like mindfulness, yoga, or breathing exercises can help manage stress, which often worsens allergy symptoms.
Remember, chronic allergies don’t define you—they’re just one part of your health journey. With the right care, awareness, and lifestyle choices, you can take back control and live symptom-free most of the time.
When to See an Allergist or Doctor
While mild allergy symptoms can often be managed at home, there are times when professional help is necessary. If you experience frequent, severe, or unexplained allergic reactions, it’s important to consult an allergist.
You should see a doctor if:
- Over-the-counter medications don’t provide relief.
- You experience difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- You’ve had an anaphylactic reaction before.
- Your allergies interfere with sleep, work, or daily activities.
- You’re unsure what’s triggering your symptoms.
An allergist can perform detailed tests to identify your specific triggers and create a personalized treatment plan. In some cases, immunotherapy might be recommended for long-term relief.
Don’t wait for your symptoms to worsen before seeking help. Early diagnosis and proper management can prevent complications and improve your overall quality of life.
Myths and Misconceptions About Allergies
There’s a lot of misinformation surrounding allergies, and it’s easy to fall for myths that can actually make symptoms worse. Let’s debunk a few common misconceptions.
Myth 1: You can outgrow all allergies.
While some childhood allergies—like milk or egg allergies—may fade over time, others (such as peanut or shellfish allergies) often last for life.
Myth 2: Allergies aren’t serious.
Even mild allergies can escalate. A small rash can become a severe reaction without warning, especially if the allergen exposure increases.
Myth 3: If you didn’t have allergies as a child, you never will.
False. Allergies can develop at any age due to environmental changes, hormonal shifts, or new exposures.
Myth 4: All natural remedies are safe for allergies.
Not necessarily. Some herbs or supplements can cause reactions or interact with medications. Always consult your doctor before trying new remedies.
Myth 5: Moving to a new area will cure your allergies.
While it might bring temporary relief, allergens exist everywhere. You might even develop new sensitivities in your new environment.
Understanding the truth about allergies helps you make informed decisions and take the right precautions
Future of Allergy Research and Treatments
The world of allergy research is evolving rapidly. Scientists and medical experts are working tirelessly to uncover the root causes of allergic diseases and develop more effective, long-lasting treatments. The goal is not just to manage symptoms but to find ways to prevent allergies—or even cure them altogether.
1. Personalized Allergy Treatments
One of the most exciting advancements in modern medicine is the rise of personalized or precision medicine. This approach focuses on tailoring treatments to an individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and specific immune response. Instead of a one-size-fits-all antihistamine, future allergy management could involve customized therapies designed specifically for your immune system.
Genetic testing and molecular allergology are already helping doctors identify allergens at the molecular level, allowing for more accurate diagnoses and targeted immunotherapy. This means fewer side effects and better long-term outcomes.
2. Oral Immunotherapy (OIT)
Oral immunotherapy is a groundbreaking approach currently being used for food allergies, particularly peanut and milk allergies. The idea is to give patients tiny, controlled doses of the allergen orally, increasing the amount gradually over time. This helps the immune system become less sensitive to the allergen, significantly lowering the risk of severe reactions.
OIT isn’t a permanent cure yet, but it offers hope to millions who live in fear of accidental exposure. It’s a major leap toward helping people tolerate previously dangerous foods.
3. Biologic Drugs
Biologic medications, such as omalizumab (Xolair) and dupilumab (Dupixent), are changing the landscape of allergy treatment. These drugs target specific molecules in the immune system that trigger allergic reactions. They’ve been especially successful in treating asthma, chronic hives, and severe eczema.
As more biologic therapies are developed, we can expect them to be used for a wider range of allergies in the coming years.
4. Allergy Vaccines and Gene Editing
Researchers are also exploring allergy vaccines that could “retrain” the immune system to stop overreacting to allergens. Combined with CRISPR gene-editing technology, scientists hope to correct genetic predispositions to allergies at their source. While still in experimental stages, these innovations have the potential to revolutionize allergy treatment within the next decade.
5. Environmental and Lifestyle Approaches
Beyond medical interventions, researchers emphasize the role of early exposure and microbiome health in allergy prevention. Studies suggest that children who grow up around pets, on farms, or in natural environments develop fewer allergies due to early immune system conditioning.
Probiotics and diet-based interventions are also gaining attention as ways to build immune resilience naturally.
The future of allergy care is bright. With advancing research, we’re moving closer to a world where allergies no longer control our lives—but are controlled by science.
Conclusion
Allergies may be a part of modern life, but they don’t have to dictate how you live. By understanding what triggers your immune system, learning how to manage symptoms, and staying proactive about prevention, you can lead a healthy, comfortable life.
From pollen and pet dander to hidden allergens in everyday products, the key to controlling allergies lies in awareness and consistent care. Whether you choose medical treatments, natural remedies, or a combination of both, the goal is the same—to help your body find balance and peace.
Allergy management is not about quick fixes but about building long-term habits. Keep your surroundings clean, strengthen your immune system, and consult healthcare professionals regularly. Remember, every small step you take brings you closer to a life free from allergic disruptions.
As research continues to advance, we can look forward to more effective and personalized treatments in the future. Until then, knowledge, preparation, and mindfulness remain your best defenses against allergies.
FAQs
1. Can allergies develop suddenly in adulthood?
Yes, allergies can develop at any age. Environmental changes, hormonal fluctuations, and new exposures can trigger sensitivities that didn’t exist before.
2. Is there a permanent cure for allergies?
Currently, there’s no universal cure, but treatments like immunotherapy and oral desensitization can reduce sensitivity and even lead to long-term tolerance in some cases.
3. How do I know if I have an allergy or just a cold?
Colds typically last about a week and cause body aches and fever, while allergies persist longer and cause symptoms like itching, sneezing, and watery eyes without fever.
4. Are natural remedies effective for allergies?
Natural remedies can help reduce inflammation and strengthen your immune system, but they should complement—not replace—medical treatment. Always consult your doctor before trying new approaches.
5. Can stress worsen allergies?
Absolutely. Stress weakens the immune system and increases inflammation, which can make allergic symptoms more severe or frequent. Managing stress through mindfulness or relaxation techniques can help.

I enjoyed reading this article. Thanks for sharing your insights.