Learn about the thyroid gland, causes of hypothyroidism, warning signs, and when to get tested. Understand symptoms, treatment tips, and serious complications like myxedema—all in simple language.
If you’ve been feeling tired, gaining weight without reason, or noticing changes in your mood or skin, you might be dealing with a condition called hypothyroidism. This guide will break down everything you need to know about this common yet often misunderstood disorder—from its symptoms and causes to treatment and lifestyle strategies. Let’s dive deep into understanding hypothyroidism so you can take charge of your thyroid health.
Table of Contents
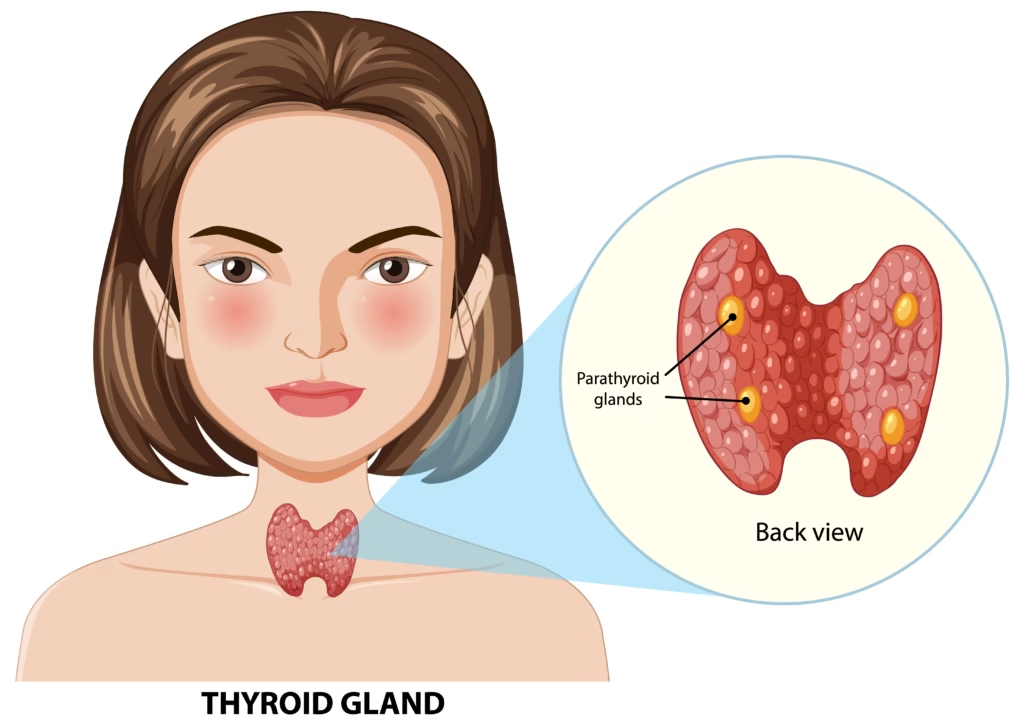
What Is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism occurs when your thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones, specifically T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). These hormones are crucial for controlling your metabolism, energy production, and even your mood. When their levels drop, your body’s processes slow down significantly.
This condition is more common in women, especially those over 30 or during hormonal transitions such as pregnancy or menopause. It’s also increasingly being diagnosed in younger adults due to better awareness and testing.
Understanding the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland that rests right at the front of your neck, just below your Adam’s apple.Despite its size, it plays a massive role in regulating many of your body’s key functions. It produces hormones that influence:
- Metabolism
- Body temperature
- Heart rate
- Energy levels
- Mental clarity
When the gland underperforms, it leads to a chain reaction of symptoms that can affect your entire well-being.
Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Recognizing the symptoms early can make a big difference in how you feel and how easily the condition can be managed. Some of the most common signs of hypothyroidism include:
- Fatigue or feeling tired all the time
- Weight gain, even without changes in diet
- Cold intolerance – always feeling chilly
- Constipation
- Dry skin and hair
- Hair thinning or hair loss
- Puffy face
- Hoarseness
- Slow heart rate
- Depression or low mood
- Menstrual irregularities or heavier periods
- Poor memory or brain fog
These symptoms often develop slowly and can be mistaken for other issues, which is why many people go undiagnosed for years.

Causes of Hypothyroidism
There are quite a few reasons why a person might end up with hypothyroidism.Some of the main causes include:
1. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
In many developed countries, the top reason behind hypothyroidism is an autoimmune condition. Here, the body’s own immune system mistakenly targets and damages the thyroid gland.
2. Iodine Deficiency
In areas where iodine is not added to salt or where diets are poor in iodine, thyroid hormone production suffers.
3. Thyroid Surgery
People who have had part or all of their thyroid removed are at high risk of developing hypothyroidism.
4. Radiation Therapy
Receiving radiation therapy to the neck—commonly for treating cancers—can harm the thyroid gland and affect how it works.
5. Certain Medications
Drugs like lithium, amiodarone, and interferon can interfere with thyroid function.
How Hypothyroidism Is Diagnosed
Diagnosing hypothyroidism is straightforward with the right tests. Your doctor will usually start with:
- TSH Test (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone): If TSH is high, it means the thyroid is underactive.
- Free T4: Measures the actual thyroid hormone levels.
- Anti-TPO Antibodies: Helps detect Hashimoto’s disease.
These blood tests are simple and widely available, making it easy to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Hypothyroidism
The standard treatment is daily use of levothyroxine, a synthetic version of the T4 hormone. It helps normalize hormone levels and alleviate symptoms.
Tips for Taking Levothyroxine:
- Make sure to take it on an empty stomach—ideally 30 to 60 minutes before having breakfast.
- Also, avoid taking calcium or iron supplements close to this time, as they can interfere with how well the medicine works.
- Stick to a consistent schedule every day
- Monitor TSH levels regularly with your doctor
Treatment is usually lifelong, but once stabilized, you’ll need only occasional blood tests to monitor your levels.
Diet and Lifestyle Tips for Managing Hypothyroidism
Nutrients That Support Thyroid Function:
- Iodine: Found in iodized salt, seaweed, dairy
- Selenium: Brazil nuts, sunflower seeds, fish
- Zinc: Whole grains, meats, legumes
- Iron: Green leafy vegetables, red meat
Foods to Watch:
- Limit raw cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cabbage) if you have iodine deficiency
- Reduce intake of soy products in large amounts
- Avoid heavily processed foods and sugars
Lifestyle Changes:
- Regular exercise helps boost energy and metabolism
- Get adequate sleep and manage stress levels
- Avoid smoking and endocrine disruptors like BPA

Special Considerations: Hypothyroidism in Women
Women are more prone to thyroid issues, especially during:
- Menstruation
- Pregnancy
- Postpartum
- Menopause
Untreated hypothyroidism during pregnancy can affect both the mother and the baby. It’s essential to monitor thyroid levels closely if you’re planning to conceive or are already pregnant.
Mental Health and Hypothyroidism
Thyroid hormones also influence brain function. People with hypothyroidism may experience:
- Depression
- Irritability
- Poor concentration
- Memory issues
Treating the thyroid often leads to improvements in mental health, making early diagnosis even more important.
Long-Term Complications If Left Untreated
While hypothyroidism is highly treatable, neglecting it can lead to serious health issues, including:
- Goiter (enlarged thyroid)
- Heart problems due to high cholesterol
- Infertility
- Myxedema is a rare but serious complication of untreated or severe hypothyroidism. It’s a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
That’s why it’s essential to take symptoms seriously and follow through with testing and treatment.
When to See a Doctor
It’s a good idea to get your thyroid levels checked if you:
- Feel constantly tired despite rest
- Have sudden or unexplained weight gain
- Are experiencing hair thinning or mood swings
- Struggle with irregular periods or fertility
Sometimes, all it takes is a simple blood test to uncover what’s going on with your thyroid.
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism is a common but manageable condition. With early detection, proper treatment, and supportive lifestyle changes, most people can live full, energetic lives. If you suspect a thyroid issue, don’t ignore the signs—speak to your doctor and get tested.
Taking charge of your thyroid health today could make a world of difference in how you feel tomorrow.
