Learn all about urine infections—causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention tips for a healthier urinary tract.

Table of Contents
What Is Urine Infection?
Urine infection, better known in the medical world as urinary tract infections (UTIs), are incredibly widespread—particularly in women. It’s a condition that many have dealt with at some point in life, and while it’s common, it’s definitely not something to brush off.
While many people try to ignore the symptoms or self-medicate, it’s important to understand that a urine infection can quickly escalate if not treated properly. In this in-depth guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about urine infections, including how to spot the signs early, when to see a doctor, and how to keep your urinary tract healthy in the long run.
A urine infection is a condition where harmful bacteria invade any part of your urinary tract, including the bladder, urethra, ureters, or kidneys. Most commonly, it affects the bladder and is referred to as cystitis
Urine infections can affect anyone, but women are at a much higher risk due to their anatomy. The urethra is shorter in women, making it easier for bacteria to travel up the tract.
Common Symptoms of a Urine Infection
Catching a urine infection early makes a big difference—it gives you a head start on getting the right treatment. Knowing what to look out for can help you act fast and avoid complications down the line.

The most common symptoms include:
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Constant Need to Pee, But Hardly Anything Comes Out
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Fever and Chills (A Sign the Infection May Have Reached the Kidneys)
- Fatigue and general discomfort
What Causes a Urine Infection?
Usually, a urine infection kicks off when bacteria—most often Escherichia coli (E. coli)—make their way into the urinary tract through the urethra and start to multiply, causing irritation and infection.
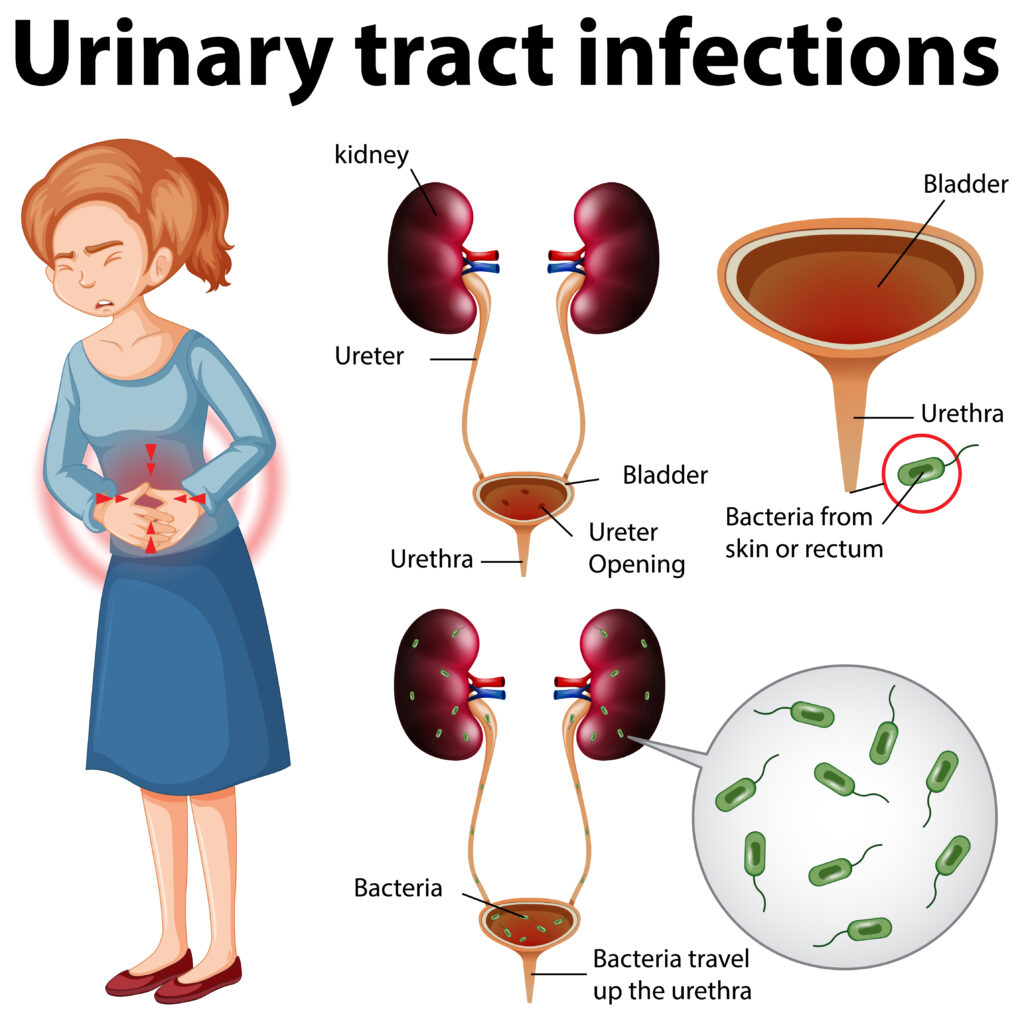
Main causes include:
- Poor hygiene practices
- Sexual activity, especially without urinating after
- Holding in urine for too long
- Use of irritating feminine products
- Wearing tight, non-breathable underwear
- Certain medical conditions, like diabetes or kidney stones
- Menopause, which can thin the lining of the urethra and reduce protective mucus
Types of Urine Infections
Understanding the type of urine infection can help guide proper treatment.
- Cystitis (Bladder Infection)
This is the most typical type of urinary tract infection, marked by a sudden need to pee, going often, and a burning feeling while urinating. - Urethritis (Urethra Infection)
Infection limited to the urethra, sometimes sexually transmitted. - Pyelonephritis (Kidney Infection)
A serious condition that includes back pain, fever, and nausea—often requiring hospitalization.
Who Is at Higher Risk for a Urine Infection?
Some groups of people are more likely to suffer from urine infections than others. These include:
- Women (especially pregnant women)
- Postmenopausal women
- People with diabetes
- Individuals using catheters
- Men with enlarged prostates
- Children with congenital urinary tract abnormalities
How Is a Urine Infection Diagnosed?
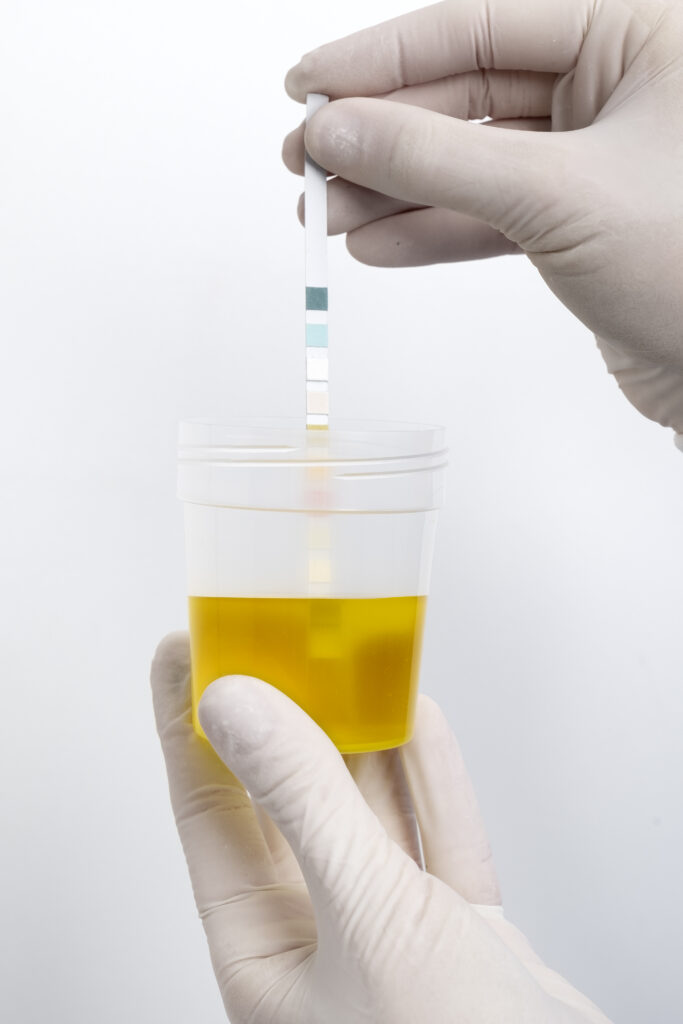
If you experience symptoms of a urine infection, your healthcare provider may perform:
- Urine Dipstick Test to Detect Infection
A simple urine dipstick test is often used to quickly check for infection by detecting certain substances in the urine that indicate bacteria or inflammation. - Urine culture to identify the bacteria responsible
- Ultrasound or CT scan if recurrent infections are a concern
Early diagnosis can prevent complications and speed up recovery.
Treatment Options for a Urine Infection
- Antibiotics
The mainstay of treatment. Your doctor will prescribe a course based on the bacteria found in your urine culture.
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
- Nitrofurantoin
- Fosfomycin
- Ciprofloxacin (for complicated cases)
- Pain Relief
Paracetamol or ibuprofen for discomfort
Urinary alkalizers to ease burning sensations
- Increased Fluid Intake
Flushing out bacteria by drinking plenty of water is crucial.
Home Remedies and Natural Support
While medical treatment is essential, several home remedies can support recovery and help prevent future episodes:

- Drink Unsweetened Cranberry Juice
- Steer Clear of Caffeine and Alcohol
- Use heat pads to relieve abdominal pain
- Practice good hygiene, especially after using the toilet and during menstruation
⚠️ Important: Do not rely on home remedies alone for active infections. Always consult your doctor.
Complications of Untreated Urine Infections
Ignoring a Urine Infection Can Cause Serious Health Issues
If left untreated, a urine infection can escalate and lead to major health complications, so it’s important not to overlook it.
- Kidney damage
- Recurrent infections
- Urosepsis (a potentially life-threatening condition)
- Preterm labor in pregnant women
Early treatment is not just about comfort—it can be lifesaving.
How to Prevent a Urine Infection

Here are simple but effective ways to prevent UTIs:
- Stay Hydrated – Drink at Least 8 Glasses of Water Daily
- Don’t hold urine for too long
- Wipe Front to Back Every Time
- Urinate after sexual activity
- Avoid using harsh soaps or douches
- Choose breathable, cotton underwear
- Manage blood sugar if diabetic
Urine Infection in Men: Why It’s Different
While less common, urine infections in men can be more serious and are often linked to underlying issues like:
- Prostate enlargement
- Kidney stones
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Men should never ignore UTI symptoms, as they may signal a deeper problem.
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a doctor if:
- Your symptoms last longer than 48 hours
- You develop fever, chills, or flank pain
- You experience recurrent urine infections
- You notice blood in your urine
- You’re pregnant or have diabetes
Conclusion:
- Take Urine Infections Seriously, but Don’t Panic
- A urine infection is common and usually easy to treat, but ignoring it can lead to serious complications. The key is early recognition, proper treatment, and good urinary hygiene habits. Whether you’ve had one UTI or suffer from them frequently, understanding your body and taking preventive steps can make all the difference.
If you’re currently dealing with symptoms of a urine infection, don’t delay—seek medical advice, drink plenty of water, and follow through with treatment.
Your urinary tract is a vital part of your health. Treat it with care!

Pingback: Pus Cells in Urine: What They Mean and Why You Shouldn't Ignore Them - Access My Doctor